No products in the cart.
The endocannabinoid system (ECS) is a vast biological neuromodulating system, comprising of receptors activating the communication between different parts of the body.
ECS transfers signals from our immune defense and central nervous system either through strengthening or weakening the signal to create homeostasis.
You can differentiate the endocannabinoid system with three parts:
- Cannabinoid receptors (CB1 and CB2)
Exists on the outside of cells. - Endocannabinoids
Activates our cannabinoid receptors. - Specialized metabolic enzymes
Breaks down endocannabinoids when used.
Cannabinoid receptors(CB-receptors)
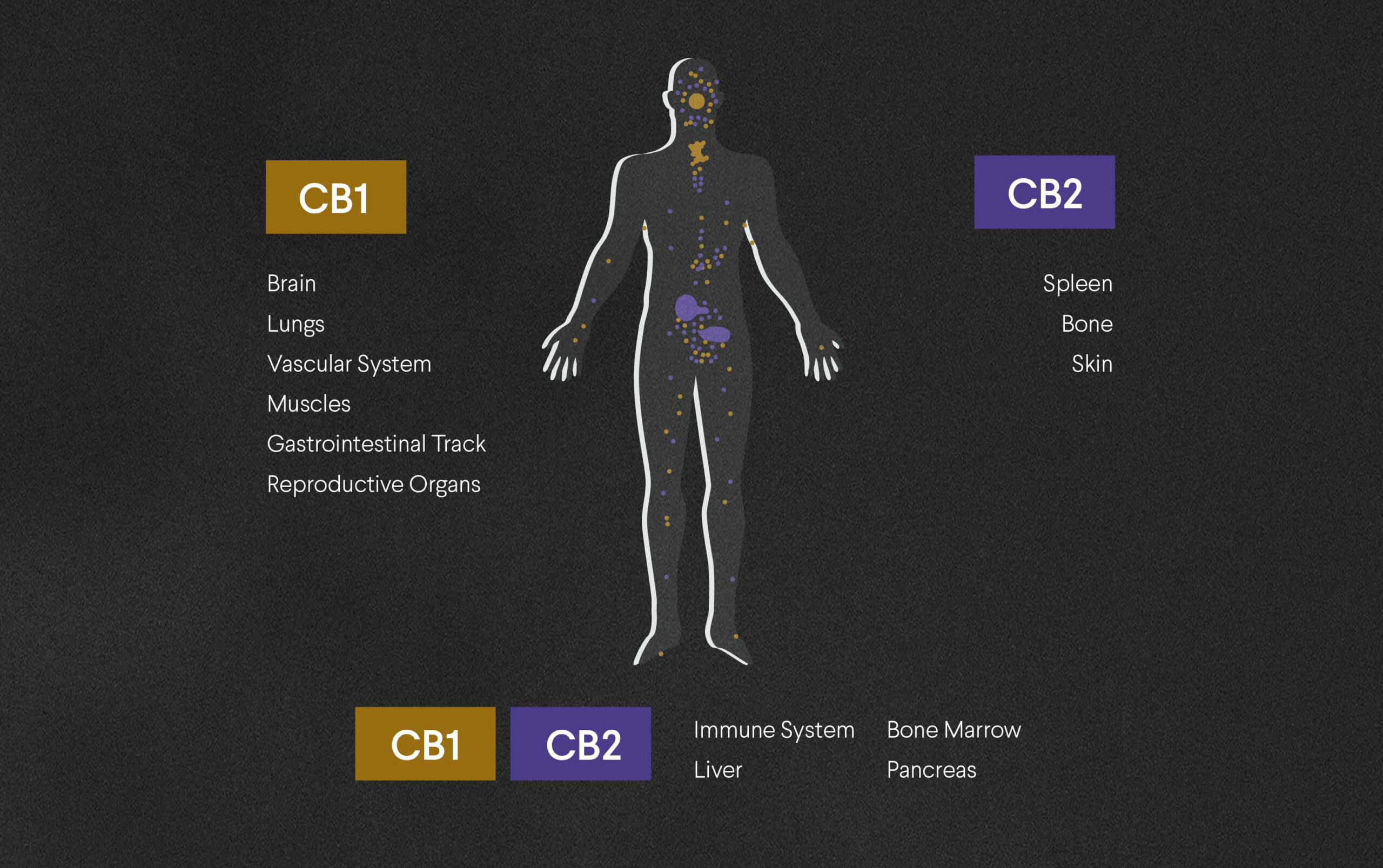
The receptors of the bodys ECS are called cannabinoid receptors (CB-receptors) and exist within most cells and organs of humans and animals.
Through research, two primary CB-receptors have been identified, these are called: CB1 and CB2.
CB1-receptors exists mainly in the brain, as well as in the central- and peripheral nervous system.
CB2-receptors exists mostly within the peripheral organs, especially cells associated with the immune defense.

Endocannabinoids are signaling molecules created in the body, functioning to regulate the endocannabinoid system (ECS). The endocannabinoids ability to traverse the synaptic gap allows them to control the release of neurotransmitters and withholding homeostasis.
The third part of the endocannabinoid system (ECS) includes metabolic enzymes, which efficiently breaks down endocannabinoids when consumed. The enzymes also make it possible for our receptors to revert into their original state; enabling the process for a new endocannabinoid to attach to the receptor, and thus a new message to be received.







Leave a comment